Why should cultural institutions do audience research?
Competition in the “museum world” is tough. It doesn’t matter how exclusive your collection is, or how famous your brand, there is competition from other cultural institutions, big and small, as well as any number of other distractions (sport, relaxation, leisure pursuits) competing for a share of potential visitors and even the most committed members’ valuable time. Face to face audience research into visitor experiences within the museum provides useful information that can be fed back into program development, museum policy and strategic planning for the future.
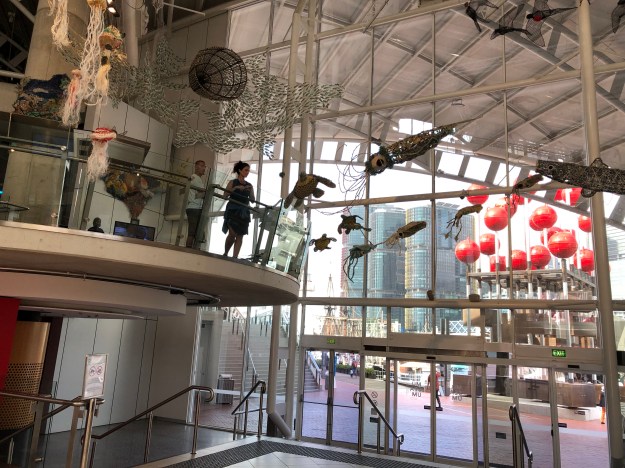

The front foyer of the newly rebranded MU-SEA-UM (Australian National Maritime Museum) at Darling Harbour
It is not enough to just happily count numbers of visitors through the door. Numbers on their own can be quite misleading without the qualitative data supporting visitor behaviour (including visitor observation and tracking – see separate post) during the visit and feedback from visitors about their personal experiences inside your cultural institution and why they may or may not come back in the future.
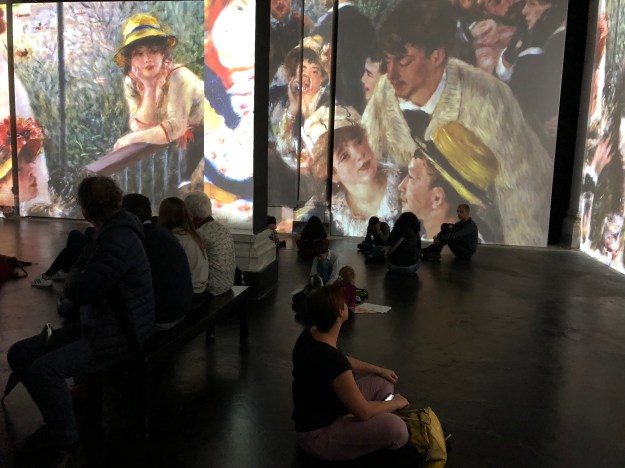

Impressionists from Monet to Cezanne at Palazzo degli Esami in Rome
Visitor Feedback Surveys
Certainly, visitor feedback is key to keeping audiences engaged with your museum and your brand. If you welcome feedback, audiences feel appreciated and valued, whether it’s about the collection, upcoming or current exhibitions, kids activities, programs, eating spaces or the state of the bathrooms!
Once you have direct communication with visitors, you can benefit enormously from their feedback (both positive and negative), but firstly, the organisation needs to be specific as possible about what it wants to know in order for the feedback to be beneficial.
Preparing your audience research objective
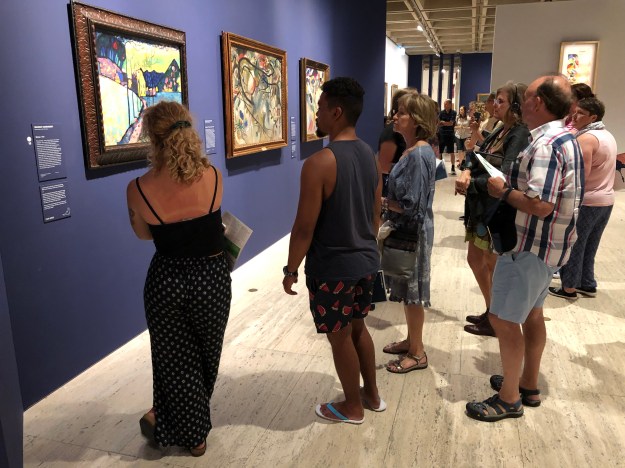

Modern Masters from The Hermitage at the Art Gallery of NSW
Feedback survey questions usually require a brainstorming session in order to define the aims of the survey. Once the aims have been determined, it becomes easier to write the survey questions. It’s impossible to retrieve and analyse data that has not been collected and there is no point in collecting data that staff have no use for. Think carefully –
- How will the information be used?
- What do staff want to find out about their visitors?
Visitor feedback survey objectives need to be clearly defined. Keep them simple and specific. Try to minimise bias in the questions. Visitor surveys are research. Research on museum visitors can determine specifics such as:
- Where are your visitors from? Are they alone or with friends/ family?
- Are they likely to return to your institution – this may be affected by accessibility. Are visitors local or from overseas/interstate? Are they already members, repeat visitors or first timers?
- What are their interests? These may be specific to your museum collection, a particular exhibition or just a family outing?
- What do people like or dislike about your museum collection, exhibitions, program and activities? Embrace both sides as an opportunity to think critically about what you offer and the way you offer it.
Also be conscious that research on people who do not visit the museum can be useful to determine why people don’t come, particularly the local community on your doorstep.
Using results
Constant self-reflection and improvement will encourage more visitors through the door. Use the findings from visitor feedback surveys to help with the planning and implementation of improvements to the “people interface” – Front of House, museum spaces and services (including facilities, cafe, museum shop etc.). Listening to and responding to the feedback findings will ensure the success of future marketing, promotional and public relations campaigns.
The solid evidence produced by analysing survey results will add credibility to your case when pitching to potential sponsors or funding sources to support future projects.
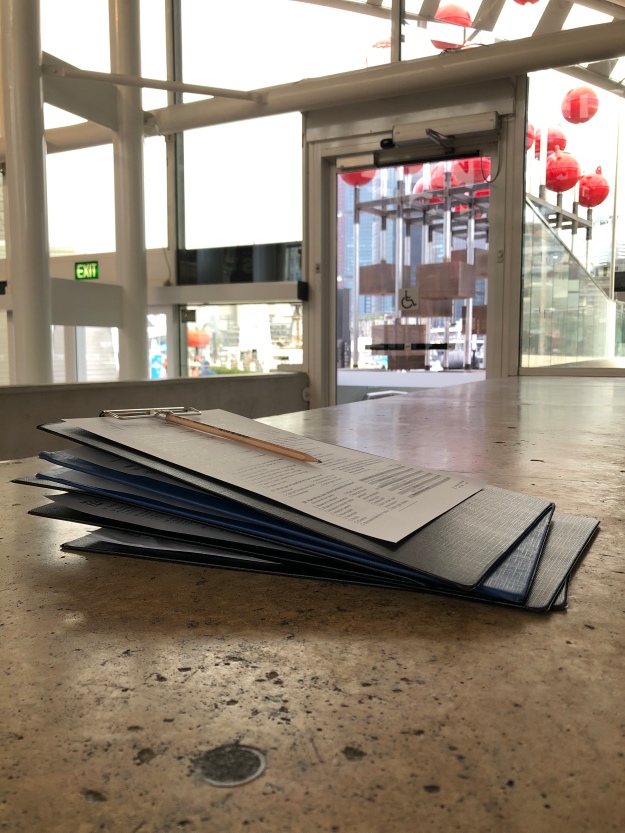

Clip boards at the ready. Many museums choose iPads for surveying. The importance thing is to use tools which allow engagement with the visitor. You may learn something extra during the exchange.
Tips for Survey staff on real time Surveying of Visitors
- Take time to absorb the museum atmosphere on the day. Move around the museum spaces and work out the best spots to catch people.
- Choose people carefully. There is no point in asking a parent with a screaming child or people preoccupied with something inside the museum where they are unlikely to want to be disturbed.
- Introduce yourself to visitors being surveyed and tell them what you are doing emphasising that the museum needs their feedback to try to improve or find out their opinion on “(whatever)” depending upon the survey aim – ticket pricing, accessibility, current exhibition content and future exhibition topics ……..
- Encourage each visitor to fill out the form themselves if possible but try to ensure that all pages are filled out
- Add “in-house” predetermined requirements such as completion time, date etc. to each survey
- Try to sample broadly
- Don’t worry about knockbacks, if you are friendly then visitors might participate next time or at another cultural institution when they have more time.
- Write down anecdotal comments which you think may add value to the survey being carried out even if the feedback isn’t relevant to the questions
- Set yourself a target based on past experience – some days are better than others depending on the flow and mood of the museum visitors on the day in question and on the length of the survey.
- Offer an incentive for their time. e.g. a coffee voucher, discount for next visit or even a voucher for the museum shop.
- Thank them for their participation
Further reading for those people thinking about visitors to cultural institutions – what visitors think and why they may or may not visit our cultural institutions.
- Potential visitors to cultural institutions are spending more time on the couch instead
- Couch potatoes, Television Consumption and Museum Visitation
https://musdigi.wordpress.com/
- Are we asking the right questions?
- 10 reasons to visit a museum
https://www.colleendilen.com/2009/07/31/10-reasons-to-visit-a-museum/
- 21 Reasons why I hate Museums
https://www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/lists/21-reasons-why-I-hate-museums/
- Why don’t people visit museums more often?
https://rereeti.wordpress.com/2015/02/03/why-dont-people-visit-museums-more-often/
- How to encourage people to visit museums more often
- The drop in museum visitors reveals a nation without aspiration or hope
https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/jonathanjonesblog/2017/feb/02/drop-uk-museum-attendance
- Audience Research 101 – #museumeval
https://musdigi.wordpress.com/2016/09/16/audience-research-101-museumeval/
- Visitor research at Te Papa
https://www.tepapa.govt.nz/sites/default/files/4-visitors-survey_0.pdf

Group tour of Hadrian’s Villa at Tivoli outside Rome. UNESCO World Heritage site.