When Paul Knight addressed the National Trust election forum late last year, he encouraged a new approach when considering Aboriginal cultural heritage. As I read his words, I saw that it applied not just to Indigenous Australian cultural heritage but on thinking critically about Australian “cultural heritage” in general.

Knight states that it isn’t just the buildings and objects that matter but rather “ the stories of place, the stories of people and the relationship that we have with that place”.
There are significant and great losses of cultural heritage from every layer of Australian history – Indigenous, Colonial and Multicultural. When you dissect the outcomes, it is so much more than just a loss of a habitat or a building or an object – it is that every single loss becomes magnified in the context of a much larger jigsaw of place and/or landscape. How does the destruction of heritage buildings or removal of a group of trees change the feel of a street or the city CBD or the suburb that we live in or indeed the landscape that they were once part of? Imagine The Rocks in Sydney CBD being flattened and replaced with high rise buildings. How much harder would it be to tell the stories of early Sydney town without its original streetscape? How wonderful it is to be able to visit the towns of Indigo Shire and Ballarat in Victoria which exhibit intact cultural heritage (houses, gardens, historic buildings) as a backdrop to the stories of Australia during the gold rush times.

Knight talks about individual sites and their connection to the greater surrounding area and that loss of context and connection impacting upon the total heritage landscape. It’s so true. As we redevelop and clear and subdivide and dig – we permanently change not only the surface area of the landscape (whether forested or built) but the archaeological landscape below the surface. The eventual “cover up” causes irreversible damage and may include the loss of the evidence to tell “tangible” stories attached to the history of that place. Archaeological finds are so critical for research and interpretation of the past lives lived right under our feet.
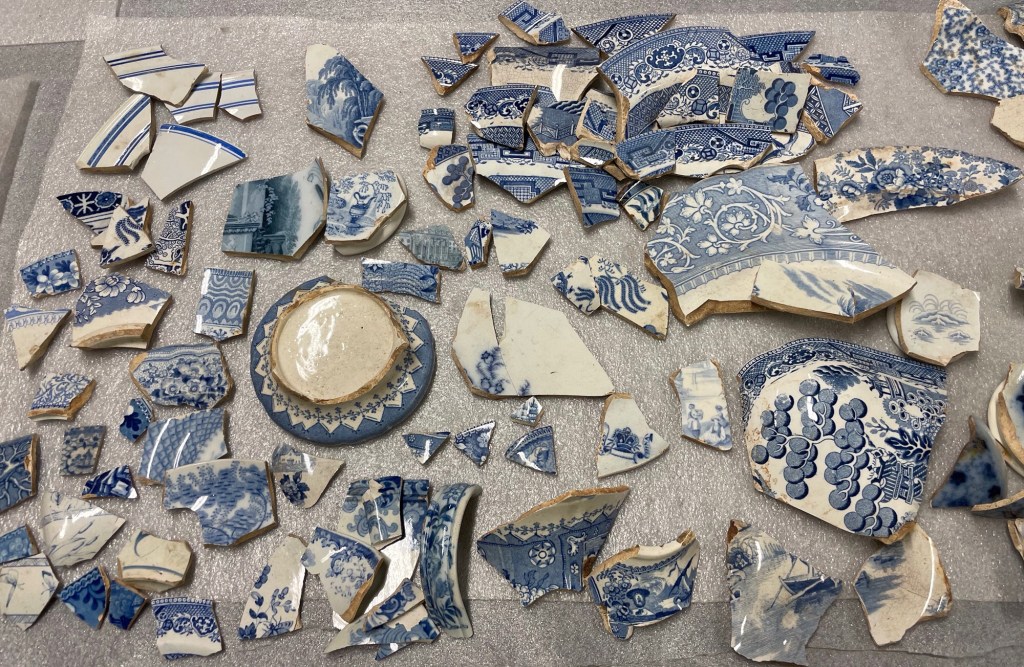

Indigenous Australians talk of their connection to “country” and being custodians of the land – I really get that. We need to pay attention to this way of seeing Australia – not only being connected to the landscape but to the built environment and other layers of Australian history (“warts and all”). We must all adapt to a different way of thinking – realising that we are all the caretakers of our cultural heritage and are just passing through. For future generations there needs to be stories and a connection to the past. We must ensure that we protect all the layers of cultural heritage and rethink the model of protection for individual sites and objects and assess them as part of the whole heritage landscape rather than case by case examples.
Heritage Legislation is critical in ensuring that Australians are custodians of their own history. We all need clear guidelines about the ways we can protect the past at both state level and a national level and including shipwrecks and our sunken past off the coast.
The State of Victoria has lead the way educating us about the past by building its Victorian Collections Platform – cataloguing and interpreting archaeological and heritage finds. The information is accessible to everyone online. Food for thought?
Recommended reading and Heritage Platforms
Australian Archaeology Resources
Parramatta Archaeology Sydney Metro
Australian Society Historical Archaeology
Investigating Heritage Significance NSW
The Multicultural Australian Colony: not just convicts

